Overview
Chinese Name: 五代
English Name: Five Dynasties, Wu Dai
Duration: About 907 AD – 979 AD
Dynasties:Later Liang 后梁 (907–923), Later Tang 后唐 (923–937), Later Jin 后晋 (936–943), Later Han 后汉 (947–951), Later Zhou 后周 (951-960)
Brief Introduction
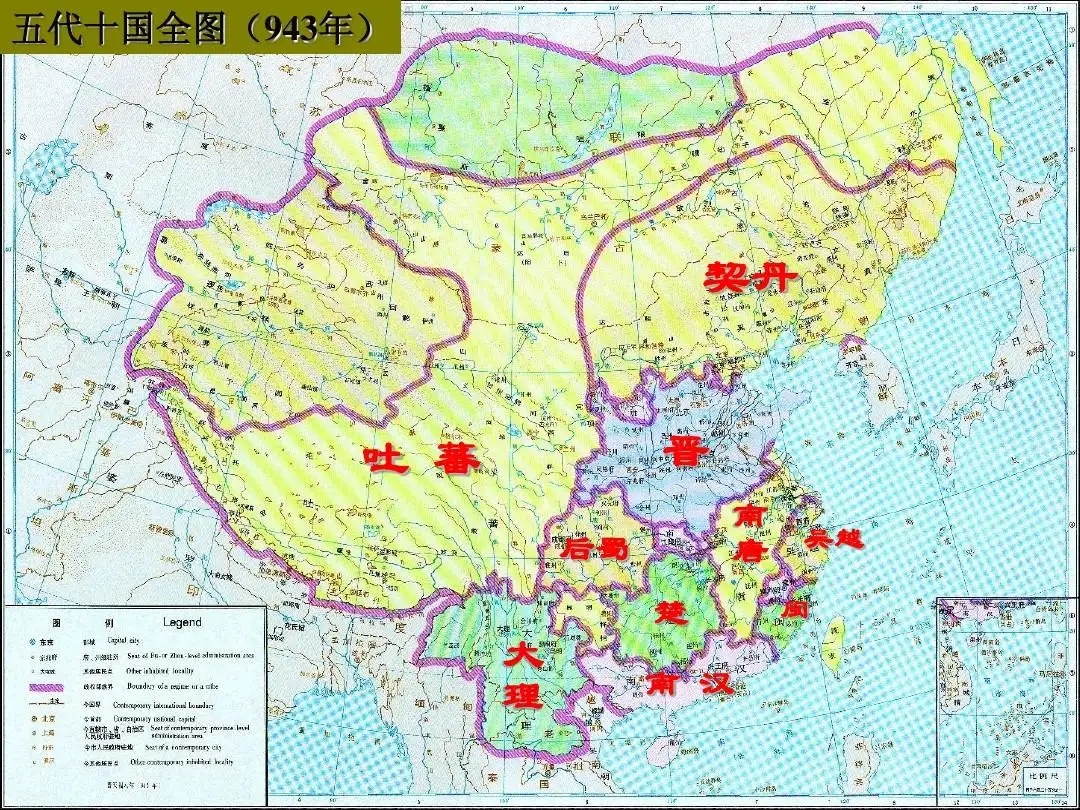
The Five Dynasties 五代 (907-960) is not a certain Dynasty, but a special historical period between the Tang and Song dynasties. After the demise of the Tang Dynasty, there appeared in the Central Plains successively the Later Liang 后梁 (907–923), Later Tang 后唐 (923–937), Later Jin 后晋 (936–943), Later Han 后汉 (947–951), and Later Zhou 后周 (951-960) whose capitals were Kaifeng 开封 and Luoyang 洛阳.
At the same time, there were 10 regimes, including Former-Shu 前蜀, Later Shu 后蜀, Southern Wu (Yang Wu) 南吴(杨吴), Southern Tang 南唐, Wu Yue 吴越, Min 闽国, Southern Chu (Machu) 南楚(马楚), Southern Han 南汉, Nanping (Jingnan) 南平(荆南), and Northern Han 北汉, which were divided into Jiangnan, Lingnan, and Hedong. They are collectively known as five dynasties and ten countries.

The Five Dynasties refer to the Five Dynasties located in the Central Plains. Orthodox historians generally call the Five Dynasties the Central Plains Dynasty and the Ten Kingdoms the separatist regime.
Major Historical Events
Later Liang 后梁 (907–923)
The Later Liang Dynasty (907-923) was the first dynasty of the Five Dynasties. In April, 907, Zhu Wen 朱温, King Liang, was abdicated by the Emperor Ai of the Tang Dynasty 唐哀帝 and was proclaimed the emperor of the founding of the people’s Republic of China, and the country’s name was Liang. In order to distinguish it from the Southern Liang Dynasty (Xiao Liang), it is called Later Liang in history.
The Tang Dynasty officially fell, and Chinese history entered the period of the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms. The Later Liang Dynasty made Kaifeng it’s capital (now Kaifeng, Henan Province), and later moved its capital to Luoyang.
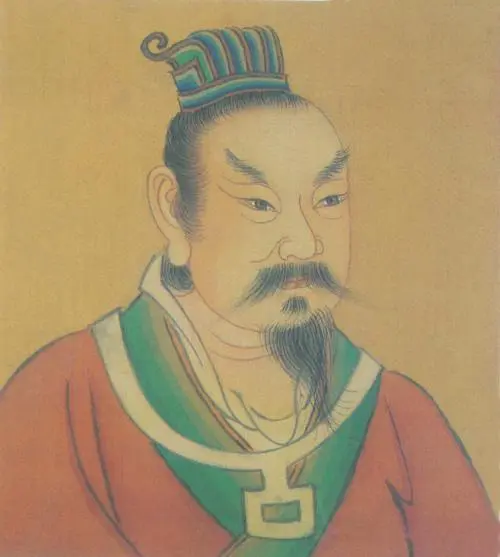

Zhu Wen was finally killed by his second son Zhu Yougui 朱友珪 in June 912. Then Zhu Yougui was immediately overthrown by his brother Zhu Youzhen 朱友贞. After this civil strife, Later Liang gradually declined, and finally died in October 923 at the hands of the old enemy Emperor Zhuangzong of Later Tang 唐庄宗.
The territory of Later Liang was the smallest of the Five Dynasties. It is bounded by the Yellow River in the north, the sea in the East, the Huaihe River in the Qinling Mountains 秦岭淮河 in the south, and Guanzhong in the West. However, the border is unstable and wars are frequent.
Later Tang 后唐 (923–937)
The late Tang Dynasty (923-936) was a feudal dynasty established by the Shatuo nationality 沙陀族 during the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms period, and its capital was Luoyang (now Luoyang, Henan). It was handed down to four emperors for fourteen years.
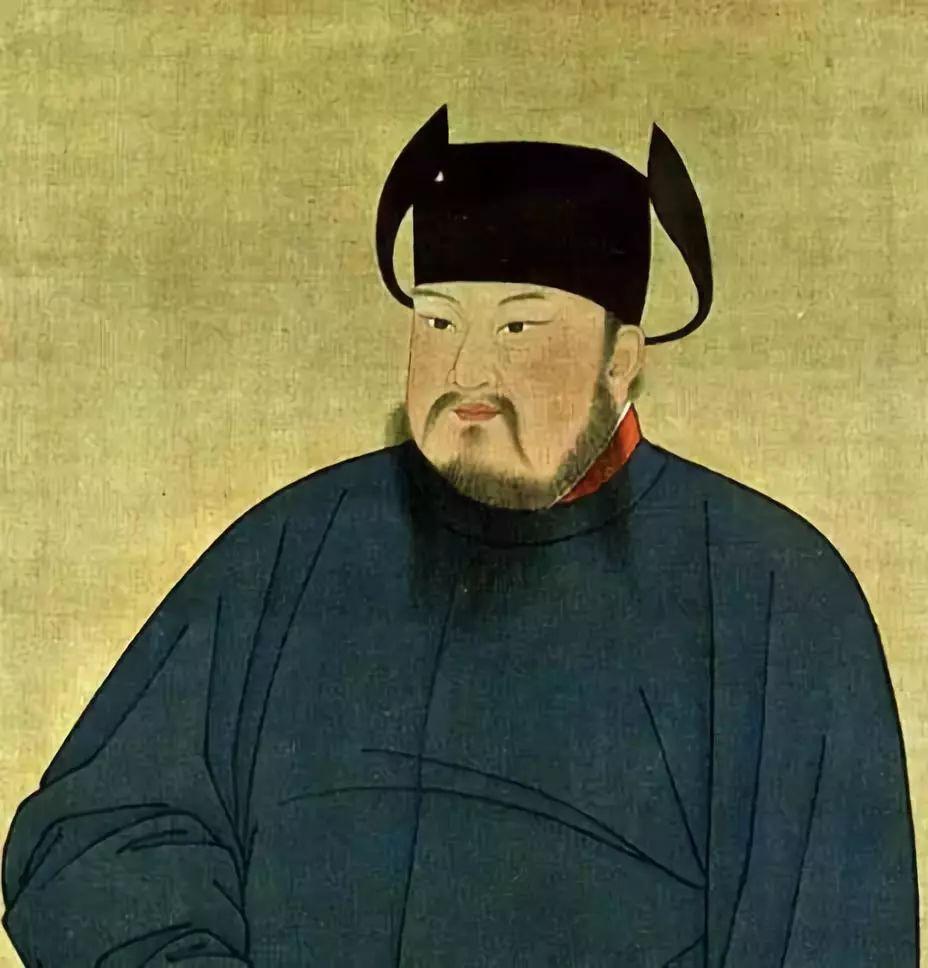

In 896, Li Keyong 李克用 was crowned king of Jin 晋王, and from then on He Dong was separated. In 907, Zhu Wen usurped the Tang Dynasty and established the Later Liang Dynasty. Jin became the largest separatist power in the north and regarded the Liang Dynasty as the dynasty established by the traitors, still regarded the Tang Dynasty as orthodox. Li Keyong died in 908, and his son Li Cunxu 李存勖 inherited the title of king of Jin. In 923, Li Cunxu became emperor in Weizhou (now Daming County, Handan City, Hebei Province). He used the “Tang” country name. Later generations call it the Later Tang.
Later Jin 后晋 (936–943)
Later Jin (936-947) was the third regime of the Five Dynasties. From November 936, Shi Jingtang 石敬瑭 was canonized as emperor by the Qidan People 契丹 to the fall of the Later Jin Dynasty in 947, it took a total of two emperors, 12 years. Luoyang was initially set as the capital, and then Kaifeng was moved as the capital.

In the summer of 936 AD, Shi Jingtang colluded with the Qidan People. He recognized Yelv Deguang 耶律德光, the emperor of Qidan as his father. At the cost of Youyun’s sixteen prefectures, he ascended the throne in Taiyuan 太原 with the support of Qidan. His country name is Jin, which is called later Jin in history. Shi Jingtang’s practice was opposed by many people, including his own past confidants. This also laid a hidden danger for Later Jin.
When Shi Jingtang died, he made his nephew Shi Chonggui 石重贵 his heir. After he ascended the throne, Shi Chonggui gradually separated from his attachment to Qidan. In the following years, the later Jin Dynasty fought with the Qidan nationality, winning or losing each other. In 947, Qidan went south for the third time, and Du Chongwei 杜重威, an important Minister of Later Jin, surrendered to Qidan.

In this way, the main force of the later generations will be lost. Shi Chonggui was forced to surrender, and his family was captured in Qidan. The Later Jin dynasty fell.
Later Han 后汉 (947–951)
In the later Han Dynasty (947 ~ 950), the dynasty was established by Liu Xie 刘暠 (formerly known as Liu Zhiyuan 刘知远) during the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms period. Its capital is Kaifeng prefecture (now Kaifeng City, Henan Province 河南开封).
After the fall of the Later Tang Dynasty, Shi Jingtang established the Late Jin Dynasty. He appointed Liu Zhiyuan as the governor of Hedong. In 947, after the destruction of Qidan, the Jin Dynasty occupied the Central Plains. But because their soldiers burned, killed, and looted in the Central Plains, they lost the hearts of the people and had to retreat north.

In February of that year, Liu Zhiyuan seized the opportunity to proclaim himself Emperor in Taiyuan, still using the year of Shi Jingtang, the Emperor Gaozu of Later Jin. In June, the name of the country was changed to Han, which was called Later Han in history.
Later Zhou 后周 (951-960)
In the Later Zhou Dynasty (951-960), the last dynasty in the Central Plains during the Five Dynasties period, the capital was Kaifeng Prefecture. There are three emperors, who enjoyed ten years of the country.
Guo Wei 郭威, Emperor Taizu of the Later Zhou Dynasty, rebelled when Liu Chengyou 刘承祐, the Emperor Yin of Later Han 后汉隐帝, seized the throne and established the Later Zhou Dynasty. After Guo Wei ascended the throne, he reduced the corvee, rectified the military discipline, and cracked down on corruption, Laying the foundation for the subsequent battles.

Important Influences
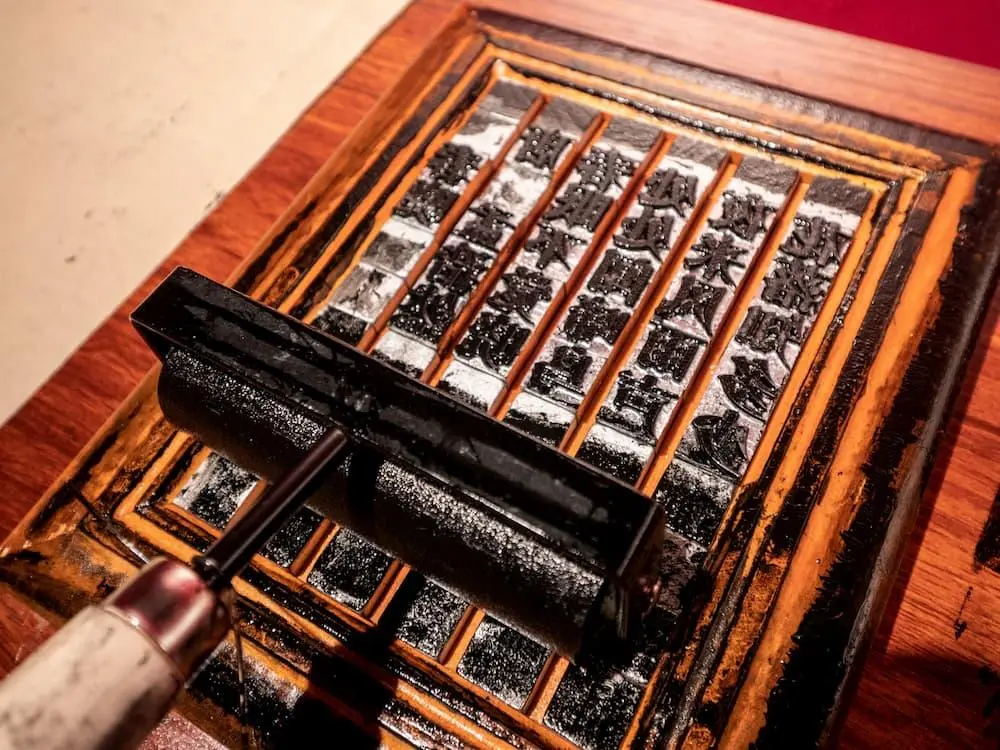
The advance in printing technique
This gave workers the idea of engraving words on a wood block and printing them with the quick development of the economy and culture in the Five Dynasties, books and other publications like calendars were needed by the public, and this demand promoted wood-block printing.
The advance in printing techniques as well as the demand from an urban public made it necessary and possible for vernacular literature to become more widespread than ever before.

Historiography has made important achievements
The book of the old Tang Dynasty 旧唐书 is the most important historical work written in this period. It has preserved a large number of original materials of the Tang Dynasty and has been valued by historians of later generations.